DNP course spotlight

DNPP 7600: Clinical and Theoretical Applications
An essential course in A.T. Still University's (ATSU) Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) program, Clinical and Theoretical Applications serves as a mentoring guidepost course, as most of the learning takes place during a student’s clinical hours. The learning that takes place embodies the true essence of the ATSU-CGHS curriculum with its direct and synchronous application of learning to the workplace. One of the core components of the course is the acquisition of direct clinical practice hours outside of the University and the student’s primary workplace. These clinical hours allow the student to practice their skills as a nurse leader. These required hours are completed under the guidance of expert nurse practitioners and educators in the ATSU faculty, as well as a site preceptor. Choosing a site for completion of the clinical practice hours can be a challenging but also a rewarding aspect of the course for students.
“Students are encouraged to utilize their network to find an area of interest or one for which they have a passion. Students have the freedom to select sites and preceptors with the exception of their current department or unit where they work to avoid a conflict of interest.”— Dr. Nicole Webb, Chair and Associate Professor of the DNP program.
Assignments for the course include reflective journal entries as well as meetings with faculty mentors and preceptors. Because the class is taken concurrently with other DNP courses, this course allows for guided practice in the application of the leadership concepts covered throughout the curriculum. For example, taken in sequence with the DNP Project Evaluation course, the work completed in Clinical and Theoretical Applications also serves as a building block for developing the final DNP project. One of the benefits of this course is the opportunity for students to identify their project topics earlier in their DNP so they can begin to build a knowledge base and their literature review.
Journal entries provide an avenue for mentorship of students by the preceptor and the ATSU-CGHS faculty member. For example, students might want to explore new quality improvement practices or gain valuable hours within a specific department at the clinical site. These types of entries provide opportunities for students, preceptors, and faculty to collaborate in creating a rewarding and productive clinical experience. These entries also allow students to reflect on challenges that might arise during their DNP and their clinical hours. The course instructor and facilitator, Clair Lunt, DHSc, MEd, MN, RN, encourages students to use these journals as a place to collaborate with her to find solutions to these challenges together.
“The journaling certainly helps students. If you have frustrations, that's the best place to put them. I am a resource always available to students as well and tell them, ‘If you need help with something, just let me know. And we'll work it out.’ ”— Dr. Lunt
The journals completed throughout the course can also serve as a reflective tool to consider when selecting the topic for the DNP project. After identifying a relevant issue through effective gap analysis, students can choose to focus their primary research on evaluating and addressing healthcare concerns.
“Staffing is the biggest challenge that nursing faces across the world. A Doctor of Nursing Practice can certainly provide people with leadership skills to address the issue of staffing shortages. For example, students can choose to use their DNP project to explore retention strategies. Our goal is to create nursing leaders that are solution-oriented and patient-centered.” — Dr. Lunt
Course Spotlight

DHAD 8800: Strategic Change Management for Health Care Organizations
An executive course in the Doctor of Health Administration (DHA) program and a pathway course in the Master of Health Administration (MHA) program, Strategic Change Management for Health Care Organizations teaches student teams how to strategically position healthcare organizations for the future using a project-based learning model. Course instructor John Fick, EdD, FACHE, intends this project to apply to each student’s learning as well as their individual career goals.
“We put students in a real-world situation so at the end of the 10 weeks, they can then say, ‘This is something I can put in my academic portfolio, and I might even be able to use it at my place of employment.’” — Dr. Fick
Dr. Fick has implemented a variety of modalities into course assignments, refined over his 14 years of developing and teaching the Strategic Change Management course at ATSU. In addition to the course-long project which tasks student teams with developing their own strategic plan, assignments include discussion, readings, reflections, a presentation, and creation of a course impact video. Students find the course informative as well as applicable to a variety of real-world contexts.
“The course concepts can not only be used for the expansion or retraction of healthcare services but can also be applied to state governments to assess the need for existing or proposed services.” — Sean Murphy, MBA
Students especially appreciate that DHAD8800 offers a lot of depth, tasking them with considering any external, competitive, and internal factors that impact the strategizing process. External dynamics considered include technological, social/cultural, demographic, political/regulatory, and economic forces.
“The real-world application of the strategic planning process, specifically the requirement to assess the internal and external environment, is an insightful aspect of this course. The process of identifying strengths and weaknesses of an organization is a difficult, but necessary, function of anyone in a leadership position.” — Alicia D. Potter-Burk RN, BSN, MS, EdS
As in the workplace, students will not cultivate their strategic plan alone, but with others. Their collaboration skills are developed as the course culminates with the groups presenting their strategic plan to a live audience with a relevant background in strategic planning.
“Most students have been on the implementation side of a strategic plan but haven’t yet been exposed to the front end of forming a plan. Reviewing the mission and the vision statements, the collected data on the external environment, the internal information, the competitor information, and more to form a strategy are all new experiences they gain.” — Dr. Fick
Students also appreciate the opportunity to connect in real time with the course instructor, offering them the chance to refine their strategic plan and return to their workplaces with confidence and fresh ideas.
“The chance to be fully involved, and then being able to go back and contribute in a new way to their organizations is a big takeaway for students.” — Dr. Fick
Seeing students’ ability to apply their learning immediately to their careers has been a satisfying outcome for Dr. Fick, and a mark of success for the course.
“I've had students say, ‘I went back and revisited our mission and vision and I talked to the person responsible for that, and shared my strategic thinking map and they're going to follow up with me.’ This course has had an impact on students in terms of the visibility in their workplaces.” — Dr. Fick
AT Course Spotlight

ATRN 8160: Contemporary Issues in Athletic Training
Contemporary Issues in Athletic Training is a course offered as a part of the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program and the Graduate Certificate in Athletic Training Education. This course explores modern issues that athletic trainers face, with a focus on contemporary concerns in athletic training education. “Students will develop insights and discuss implications for the ever-changing nature of health professions education,” according to the course description. ATRN 8160 is a dynamic course which allows flexible curriculum content in order to address professional priorities and trending concerns in higher education as well as the industry as a whole.
“ATRN 8160 helps students understand the direction in which the profession of athletic training is going, as well as barriers to moving forward and ways we can make a change. I was able to implement knowledge from the course into my workplace by taking these topics to my coworkers and encouraging change in their individual practice.” — DAT student, Kelly Ferian DAT, LAT, ATC
Some of the recent contemporary issues explored in this course include the student debt crisis as well as the evolving nature of faculty roles in the athletic training education space. All issues are explored globally and objectively, and students are encouraged to speak their minds in the safe environment instilled by Sara Brown, MS, ATC and Cailee Welch Bacon, PhD, ATC, FNATA, the course instructors. In order to make sure the content is applicable to students, Professors Brown and Welch Bacon present several issues and the class then votes on which topics will be explored in the course each block.
“I was able to implement knowledge from ATRN 8160 immediately. I took this course during the COVID-19 pandemic and found the information to be useful in navigating healthcare resources for student athletes. I felt more comfortable participating in conversations I would not have before.” — DAT student, Rebecca D.
Assignments in ATRN 8160 are multi-modal and dynamic, with a heavy focus on discussion. The course was designed with this emphasis in mind, so that students may bring their own work experiences and work culture to the classroom environment, where they can then learn from and be supported by a cohort of ATs from various backgrounds.
“Our classroom environment is so dynamic because we have students from every athletic training setting and every type of experience, coming from a wide range of years of experience in the profession. In this unique environment, multiple perspectives are considered continuously throughout the course.” — Cailee Welch Bacon, PhD, ATC, FNATA
ATRN 8160 students are also given a thoughtfully selected series of reading assignments, composed of eight books related to diversity, equity, inclusion, and other crucial concerns in the athletic training profession and in higher education. The course culminates in a professional priorities project, in which students are tasked with identifying the top three issues facing the athletic training profession. They then must reach out to athletic trainers in different settings and with differing experience levels in order to get more perspective on professional priorities and issues identified by current ATs. Toward the end of the course, students take this insight and apply it toward a deep dive into their chosen issue to explore, proposing solutions in the process.
“ATRN 8160 encourages students to think broader about many issues in AT with applicable topics to every setting. I found the tenure assignment to be especially helpful in my current workplace and was even able to use the knowledge learned to gain a promotion at work. I am a better professional for taking this course and for having the opportunity to work with and learn from Professors Brown and Welch Bacon.” — DAT student, Chelsea P., MS, LAT, AT
The Athletic Training Department strives to prepare ATs to take on modern challenges in any setting. Through discussion, careful reading, and professional outreach, the Contemporary Issues in Athletic Training course prepares students to not only better understand the professional issues faced by those in the field, but to also address these concerns and advance the AT profession as a whole.
MHSc Course Spotlight

MHSC6300 Special Topics in Health Science Research
The Master of Science in Health Sciences (MHSc) program offers a Special Topics in Health Science Research course (MHSC6300), which is designed as an introduction to using the research process to address health science problems and the use of evidence as a foundation for practice. The course is designed to provide students with practical skills they can apply to their professional role, whether they are in a clinical, managerial, or leadership position.
“This course teaches students to not just read, but critically appraise research so they can discern whether it's a high-quality piece of evidence and see if the topic was addressed in a rigorous way.” – Professor, Dr. Kathleen Mathieson, PhD, CIP
Special Topics in Health Science Research engages students in each step of qualitative and quantitative research design, from forming a methodology all the way to data collection, analysis, and presentation. The course is structured in 10-week blocks and is asynchronous, meaning students can complete the course at their own pace and on their own schedule.
Throughout the course, students engage in critical analysis of various research topics in the health sciences and create an integrative literature review. They also investigate a health science problem or area of improvement relevant to their professional role or personal interest and come up with a plan for how they might research and address the specific question related to the problem. There are also assignments in every module, including discussions focused on specific types of research articles, an infographic assignment, and analyzing a systematic review article.
“This course is of great importance to me due to it expanding my knowledge regarding research methods. I learned many new concepts that are needed for my future studies. The M9 assignment was my favorite, as the research was related to my field. The discussions were always engaging.” – MHSc student, Kamar E.
Students also contribute to a wiki where they gather and share research resources that they find useful, and this helps them build a credible repository of research resources that they can utilize after they’ve completed the course and MHSc program.
Overall, the course provides students with a strong foundation in research methods and equips them with the skills needed to critically analyze and evaluate research in the health sciences. By the end of the course, students are able to apply what they have learned to their specific interests and roles and engage in meaningful dialogue about research.
MEd Course Spotlight
.png)
Innovative Teaching Strategies in Health Professions
Taught as part of the Master of Education in Health Professions (MEd) program at A.T. Still University’s College of Graduate Health Studies (ATSU-CGHS), Innovative Teaching Strategies in Health Professions discusses traditional and emerging learning theories in pedagogy and andragogy. This 10-week course is fully online and asynchronous.
Innovative Teaching Strategies in Health Professions covers the most effective, commonly used, evidence-based teaching strategies in health professions education. Topics discussed include student-centered learning, heutagogy, pedagogy 2.0 and 3.0, problem-based learning, and transformative learning. Students study the differences between instructor-focused and student-focused teaching strategies and learn how to meet a variety of learning needs and learning styles so information can be effectively understood by all students.
“The slow introduction into the different teaching styles was the most insightful aspect of this course. The lesson plan assignment was my favorite, because it makes you evaluate and analyze what you have learned.” – MEd student, Aaron B., MSDH
Emphasis is placed on teaching and learning in the face-to-face, hybrid, and online learning environments, and learning how to differentiate teaching strategies.
Learning activities include written assignments, reading articles published in professional journals, and watching videos, in addition to didactic teaching from the instructor. Interactive discussions are also a large part of this course, offering students the opportunity to share their knowledge and expertise with each other in the context of in the context of subject discussion topics each week.
There are a handful of other written assignments, including blogs, journals, papers, and a teaching presentation, where students design a teaching plan that they can use in the future.
“I learned a lot about my writing in this course, and that multiple theories depend on the students and the topic being taught.” – MEd student, Ann H.
There is a constant stream of new research about the effectiveness of various teaching strategies being published, so course content and learning materials are continuously updated.
DPT course spotlight

DPTP 8807: Radiology and Imaging
Taught as part of the Postprofessional Doctor of Physical Therapy program, Radiology and Imaging is a three-credit course instructed by Wayne Smith, PT, DPT, MEd, Board-Certified Sports Clinical Specialist, Registered Musculoskeletal Sonographer and Colin Rigney, PT, DPT, Board-Certified Orthopaedic Clinical Specialist, Registered Musculoskeletal Sonographer.
“Dr. Rigney is a very good instructor. The course was challenging, and it required a lot of focus and dedication to learning. Through Dr. Rigney's expertise, I was able to understand the material and appreciate its value in providing quality patient care. I enjoyed doing the assignments, and it stimulated my critical thinking skills. This course was tremendously helpful, and I am very grateful that I attended this class.” – DPT student
This course covers the study of the common diagnostic and therapeutic imaging studies such as radiographs, CAT, MRI, and musculoskeletal imaging. Providing students with the necessary knowledge about imaging modalities, this course teaches how to read the images, how to look critically at the anatomy of the image, how to use imaging in therapy, and what imaging options would be most beneficial for a patient.
“The class was well-organized. Assignments and discussion board posts were applicable to clinical scenarios and helped me to be a better-informed clinician. I am particularly grateful for the video tutorials by Dr. Rigney and Dr. Smith. As someone with no formal or informal training in reading imaging studies, I learned a lot of new information.” – DPT student
This course teaches students to become aware of the indications and implications of commonly used diagnostic imaging tests as they pertain to patient/client management. Students find the presentations and audio-video training tutorials especially valuable. The professors cover various aspects of required clinical skills during imaging.
It’s not common to see a physical therapist in the field ordering x-rays and looking critically at a diagnostic image, as it’s not the standard practice in the profession yet. This course offers a great opportunity to bridge that gap and set an example for the rest of the profession.
“This course has been an eye opener for how imaging can impact therapy assessment and intervention. The materials provided were very thorough and well thought out. The subject seems very intimidating but the program itself is well organized and focuses on the most important aspects that are essential for the PT practice.” – DPT student
Radiology and other imaging modalities are great tools for PTs to use to expand their scope of practice.
“This course was really challenging, and we were propelled to not be shy in creating our own opinions and decisions as physical therapists. Therefore, I think it is of significant value to be a part of this class and have a teacher as an example of a great therapist. I would not change anything in this course, and I could not be more pleased to be a part of it.” – DPT student
AT course spotlight

ATRN 8150: Winter Institute
The Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program encompasses a four-day intensive Winter Institute at A.T. Still University’s Mesa campus. This is the only on-campus requirement of the DAT program. At this in-person event, students come together to meet faculty within the Athletic Training Department and adjunct faculty who are leaders within the profession.
Focused on advancing athletic healthcare, the thread of innovation is woven throughout the course with particular emphasis on innovation to advance higher education, patient care, and research. Each day of the four-day institute is dedicated to a different concept centered around faculty and industry leader presentations and small group discussions.
“The types of conversations we have at the Winter Institute can lead to change, advancement, and progression of the AT profession. I was able to come back to my workplace and have meaningful conversations with my colleagues about best practices, and I was able to speak with my supervisor about specific ideas to improve the care we provide.” – DAT student, Kimberly D., MS, ATC
This course is designed to promote in-depth interaction between students and faculty to facilitate the development of action plans for leading innovation in athletic healthcare education, patient care, and research.
The Winter Institute includes a presentation in which students prepare a project proposal specific to their work environment with the opportunity to receive feedback on the feasibility of implementation to help them develop the knowledge and skills needed for leading innovations within their own healthcare facilities and institutions. For many students, the Winter Institute is when it all clicks.
“The broad selection of topics discussed during the Winter Institute led me to generating new ideas to implement into my clinical practice, with the goal of continuing to offer the best patient care. The study group sessions were my favorite part of the Winter Institute, because I was able to hear everyone’s perspective on different topics and share different points of view.” – DAT graduate, Adriana P., DAT, LAT, ATC
The Institute faculty consists of leading innovators in athletic healthcare from across the country. Each faculty member leads educational sessions in their respective area(s) of expertise and also serves as small group facilitators. The face-to-face time with faculty promotes a new level of getting to know each other from a professional and personal lens.
“It’s nice to come together and see classmates and faculty in person. I think the Winter Institute really consummates all the learning by bringing it all together. Providing the opportunity to have those high-level discussions in the profession and how the learning students do every day can help solve some of those problems is a really powerful experience.” – Director of student recruitment and assistant professor, Dr. Nikki Harris
Throughout the week, students will be a part of small groups that meet daily, each facilitated by an internal (ATSU) and external faculty member, to maximize opportunities for extensive interactions with peers and faculty. Project groups meet daily to help students develop their innovative projects for leading and managing environmental change. Reflection groups meet at the end of each day to discuss the key points, where students experienced their greatest knowledge gains, how the information can be translated into their work settings, and what new questions may have emerged.
“The ability to share experiences with peers and learn from the top Athletic Trainers and educators in our profession cultivated an environment that you do not get to experience anywhere else. I found each day of the Winter Institute insightful and truly could not be more grateful to have experienced it.” – DAT student, Karley P., ATC
The Doctor of Athletic Training program is student driven and changes the way ATs think about athletic training in all aspects.
“The Winter Institute inspired me to change the way I evaluate, helped me make my practice even more patient centered, and gave me the tools to bring to my administration to show them our value lies outside of practice coverage, and that our daily schedule needs to reflect that.” – DAT graduate, Stephanie T., DAT, LAT, ATC
AuD course spotlight

AUDP 8400 - Global Healthcare and Audiology
Taught as part of the Post-Professional Doctor of Audiology program, the Global Healthcare and Audiology course is a four-week guided discussion focusing on current global hearing healthcare practices, areas of need, and advocacy for effective policies and services. Telehealth in audiology and interprofessional collaboration are also explored as potential opportunities for improving access to hearing healthcare services.
Week to week, instructor Kelly Malcom, AuD, MPH leads discussion with input from the program’s global students focused on concerns about the future and sharing information from healthcare systems across the globe. Topics discussed include practitioner interest at the undergraduate level, number of practitioners going into the profession, legislature changes and changes in law across the globe, and where leaders of the profession should be focused and are needed globally.
“Learning about the latest statistics on hearing loss, causes, and prevention was very insightful. Because of this course, I can better educate patients on prevalence of hearing loss in Australia and prevention measures.”
– AuD graduate, Dr. Michelle P.
This course includes case scenarios, article reflections, discussion boards, and written assignments culminating in a final project that students build components of each week.
Because the post-professional AuD program is focused on the global practitioner, this course is an amazing opportunity to evaluate the profession of audiology globally and not only look at where the profession is now, but where it’s going in the next 10, 15, 20 years. Plus, as the profession becomes more interconnected, this course emphasizes interactions between peers and the instructor to provide discussion based on a variety of global perspectives.
An area of expertise for Dr. Malcolm, who has focused her public health research on increasing access to audiology services in the United States and in low- and middle-income countries, she has delivered audiology services in Nicaragua and assisted in creating a teleaudiology program in western Nebraska to provide auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing for infants in a rural area. Dr. Malcolm received her doctor of audiology degree from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln in 2020 and her master of public health degree with a concentration in global health from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in 2021.
“The most insightful thing about this course was looking at hearing healthcare and healthcare in general from a larger perspective.”
– AuD student, Greg F., MS, CCC-A
Since audiology is a dynamic profession with technology changing clinical practices quickly, this course helps students refocus their perspective and take a global view of the profession, rather than solely focusing on their clinic and location. With a different focus than the typical science-, counseling, and technology-based courses seen in doctor of audiology curriculum, this course is unique in its structure and application.
AuD course spotlight

AUDP 7100 – Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
Taught in the online Post-Professional Doctor of Audiology program, Neuroscience and Neuroimaging is a 10-week course designed to provide a detailed exploration of the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system upon which the foundations of audiologic diagnostic and therapeutic measures are based.
This course begins with a review of topics that students may or may not have covered at the master’s level. The weekly modules then provide an in-depth study of the development of the nervous system, the structure and function of the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system, neurovasculature, and detailed coverage of the audiovestibular system. Understanding overall function of the peripheral and central nervous system structures is geared toward making sure audiologists consider the health and medical conditions of their patients with a focus on whole person healthcare.
"I had a life-changing experience in AUDP 7100: Neuroscience and Neuroimaging. My grasp of neural processes was enhanced by this course's exploration of the intricate workings of the brain, and it also sparked a curiosity that fuels my passion for the subtleties of the human mind." – AuD student, Genia S., M.Sc.
Course topics include an understanding of imaging techniques used for the evaluation of auditory and vestibular pathologies. Neurodiagnostic imaging data from CT scans, MRI, and other imaging or data are correlated with audiologic findings when possible.
“After taking my first anatomy and neuroanatomy courses, I was hooked on learning and teaching neuroscience and neuroanatomy topics. As an audiologist, understanding the underlying structure and physiology of the nervous system is so valuable to our clinical judgements and interpretations.” – Dr. Parent-Buck
This course is taught by Tabitha Parent-Buck, AuD. Dr. Parent-Buck is a tenured professor and was appointed as the founding chair of the Department of Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology at A.T. Still University’s Arizona School of Health Sciences (ATSU-ASHS) in July 1999. She is also the program director of the Entry Level Doctor of Audiology Program. Dr. Parent-Buck obtained her BS and MS degrees in audiology from Purdue University and her Doctor of Audiology degree from Baylor College of Medicine. Prior to developing the online and residential AuD programs at ATSU, she practiced in a variety of clinical settings, worked as a representative and trainer for AVR Sonovation, and provided academic and clinical instruction as an assistant professor in the Department of Speech and Hearing Sciences at the University of New Mexico. Her main areas of teaching for online and on-campus courses include neuroanatomy and neurophysiology, embryology, genetics, pharmacology, amplification, and otoacoustic emissions. Dr. Parent-Buck has published and presented on a variety of industry topics including the AuD movement, the use of web-based educational tools, hearing aid technology, otoacoustic emissions, neuroanatomy, vestibular assessment, genetics, and pharmacology.
“The neuroscience and neuroimaging course was challenging but extremely informative. It was very in depth and definitely expanded my knowledge. I feel much more comfortable analyzing images in clinic and feel it has made me a better clinician.”
– AuD student, Annie M., M.S.
Students’ understanding is assessed through a variety of learning activities including discussion board posts, case studies, short papers, quizzes, and examinations. Learning assessments in this course provide an opportunity to share clinical experiences, expand knowledge in this area, and rethink how to apply concepts in daily clinical practice.
“I truly enjoy working with colleagues across the globe and new audiology students in all of the neuroscience and neuroanatomy courses I teach. The content keeps me energized and I never get tired of the discussions and questions about anything related to neuro.”
– Dr. Parent-Buck
This course is offered to individuals who are taking the full post-professional AuD program or as a standalone course in the non-degree seeking option for individuals who already have their AuD, PhD, or a master’s and desire to expand their neuroscience knowledge.
AuD course spotlight

AUDP 8310 - Tinnitus and Hyperacusis: Theories, Evaluation and Treatment
Taught in the Post-Professional Doctor of Audiology program, Tinnitus and Hyperacusis: Theories, Evaluation and Treatment is a 10-week course designed to provide a detailed exploration of tinnitus and hyperacusis and the clinical tools required to treat this patient population.
Tinnitus is a huge topic in audiology. In the last decade, audiologists have developed a full tool kit of what questions to ask in the case history, which diagnostic tools to choose depending on the patient complaint, and a wealth of recommendations and counseling support for patients.
“I have used various resources from questionnaires to counseling tools to help my patients who suffer from tinnitus or hyperacusis. The assignments were relative and very useful for my everyday work in private practice.” – AuD graduate, Dr. Michelle P.
Course topics include etiology, epidemiology, comorbidity, musical hallucinations, misophonia, hidden hearing loss, impact on quality of life, and exacerbating factors. Detailed case histories; tinnitus self-assessment questionnaires/inventories; hyperacusis visual analog scales; psychoacoustic measurements and self-report measures of stress, anxiety and depression will be explored. This course is filled with case studies for students to put into practice what they learn.
"I believe the involvement of audiologists in tinnitus treatment and management is paramount for the emotional wellbeing of this population. Audiologists’ extensive knowledge of the auditory system and fundamental understanding of the aural rehabilitation process position them as leaders in tinnitus care." – Professor, Dr. Pineault
This course is taught by assistant professor Dany Pineault, AuD, Msc. Dr. Pineault earned his bachelor of applied science degree in speech and hearing sciences and master of science degree in audiology from the Université de Montréal. He earned his doctor of audiology degree from ATSU-ASHS. An expert in this field, Dr. Pineault has co-authored several papers on tinnitus and hearing health problems among the adult population in Canada with research analysts at Statistics Canada. Dr. Pineault has extensive clinical experience in the assessment and management of bothersome tinnitus and decreased sound tolerance. He regularly lectures hearing healthcare professionals on tinnitus and hyperacusis treatment protocols such as amplification, sound therapy, tinnitus retraining therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, acceptance and commitment therapy, and mindfulness-based stress reduction.
“Dr. Pineault is a great professor and I really benefited from his interactions in the discussion boards. He did a great job of explaining complex issues.” – AuD student, Greg F., M.S. CCC-A
This course also includes an amazing section on the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying tinnitus and hyperacusis, where Dr. Pineault covers the physiology, anatomy, and different treatment options. Students learn evidence based audiological interventions related to tinnitus and hyperacusis treatment and management including counseling, amplification, and comprehensive management programs through the review of case studies. Students who take this course can implement the tools learned the very next day in their clinical environments.
ATSU’s post-professional AuD is meant to build on master’s level content, so Dr. Pineault reviews what individuals may or may not have learned at the master’s level and deep dives into the current research.
“The biggest takeaway is 10-weeks of knowledge about everything related to tinnitus and hyperacusis. This course is updated each block, so all references are the newest, latest research. Students discuss the most recent advances on this topic and are able to apply them immediately in their clinical environments.” – Program director, Dr. Ruotolo
This course is offered to individuals who are taking the full post-professional AuD program and as a standalone course in the non-degree seeking option. Individuals who already have their AuD, PhD, or a master’s and desire to implement tinnitus treatment can take this as a single course.
DPT course spotlight

DPTP 8831: Gender Healthcare in Physical Therapy
A key course in the Postprofessional Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program, Gender Healthcare in Physical Therapy explores the latest evidence surrounding gender-specific healthcare issues. The coursework examines and compares contemporary and traditional interventions and how they adjust alongside evolving knowledge in the field.
Taught by Heather Allen, PT, DPT, for the past 14 years, Gender Healthcare is meant to provide an overview of gender issues that may occur throughout the lifespans of males and females. Conditions covered include common pelvic floor dysfunction diagnoses, such as urinary incontinence and pelvic pain. More specific issues related to adolescence and aging in different genders, from dysmenorrhea to pregnancy and menopause in women and conditions like testicular and prostate cancers in men, are also reviewed.
“I want the therapists to be able to recognize and be aware of these health conditions so they can, at a minimum, provide education to the patient. After taking this course, they may not be 100% confident in treating pelvic floor dysfunction — but they can educate the patient on what's normal bladder physiology, they can understand exercises to assign to the patient. They can now educate patients, friends, co-workers, and neighbors on all these topics.” — Dr. Heather Allen
Dr. Allen notes that many students leave the course with a broader sense of the scope of the PT field, as well as more confidence and knowledge needed to provide whole person care.
“I learned that the scope of PT practice is much more diverse than I thought. [Some of the most helpful knowledge centered around] pediatric bladder and bowel dysfunction. I work with children and these conditions are very common with the population I work with, and so learning about this provided me with new insight.” — Jamie Lee Valdez, PT
Much of the course assignments involve creating patient educational materials, as Dr. Allen wants the students to leave with not only the knowledge but also the resources needed for students to educate their communities. Other assignments include frequent discussion, occasional quizzes, and case study assignments that require students to support recommended interventions for diagnoses with peer-reviewed literature.
“Regardless of what PT setting you work in, you can take away something from this course to apply in your clinical study.” — Dr. Heather Allen
For PTs who don’t normally diagnose gender-specific conditions, they feel the course better equipped them to take a whole person view of health for their patients and provide more holistic care.
“This course helped me feel confident understanding some of my patient's other distressing symptoms such as pelvic floor issues, osteoporosis, heart disease, menopausal symptoms, and certain cancer history.” — Shelley Hockensmith, PT, MPT, NCS
Dr. Allen’s goal of PTs leaving the course with information they can share with others is reflected in the feedback received.
“[After this course, I] was able to share information about gender specific conditions in an objective and easy manner.” — Jose Dela Cruz, PT
Gender Healthcare is a course that expands students’ scope and quality of patient care, empowering their PT practice.
“I was able to implement this course into my practice because I can now offer a basic verbal assessment and some preliminary and practical suggestions to patients [for more conditions, rather than saying] I cannot evaluate or treat.” — Jay Brahmbhatt, PT
DPT course spotlight

PT804: Integumentary Physical Therapy
A crucial course in the Postprofessional Doctor of Physical Therapy program, Integumentary Physical Therapy is an eye-opening look into physical therapists’ role in wound care, a too-often overlooked element of a PT’s realm of services. Course instructor Dana Palmer, PT, DPT, knows that many practicing PTs are unaware of how important knowledge of integumentary care is, and strives to reverse that phenomenon in this six-week course.
PT804 is divided into six modules, starting with an overview of wound care, before delving deeper into the five main types of wounds PTs are likely to encounter in clinical settings. The mid-point of the course allows students to practice their knowledge of wound debridement — which involves cutting away dead tissue so the wound can heal more efficiently — on a ham hock, eggplant, or orange. Students appreciate this practical assignment, which is evaluated over video.
“Being able to perform debridement on either a pork hock or an orange was a creative way to experience how the techniques can be performed properly. That was my first and only hands-on experience with sharp debridement, and I truly enjoyed it. I was able to apply the knowledge I gained from this course to patient/client education.” — Aileene Nejal, PT, PTA, CBIS
The fourth module picks up from debridement to discussing dressing wounds, before moving into adjunct modalities in week five — or how other PT treatment methods can apply to wound care. The final week of the course presents students with three case studies to which they can apply their integrated learning in the course by analyzing and presenting their suggested concerns, treatment, and patient education measures.
“The entire layout, organization, and content of the course were phenomenal. Before this course, I had little to no knowledge on application for wound care. Dr. Palmer’s mentorship and guidance helped me grow as a professional.” — Aishwarya Sriram, PT
PT804 utilizes many modalities to cover course material. From assigned readings to conducting their own secondary research to procure the latest evidence in wound care, students are tasked with reading widely and deeply on various literature in integumentary care. These readings are supplemented with frequent discussion, which allows students to gain insight from each other as well as their course instructor. Dr. Palmer also assigns a weekly critical thinking assignment, which challenges students to apply their learning to various case studies related to integumentary PT.
“Each weekly module had critical thinking discussions. The discussions were clinically relevant and applicable to realistic patient scenarios. These scenarios resulted in a deeper understanding of the material and the application of the new information.” — Kyle Knapp, PT, OCS, CSCS
Students in PT804 appreciated Dr. Palmer’s commitment to their learning, as demonstrated through her passion for the subject material, her availability for questions, and her additional learning opportunities and meetings available beyond class hours.
“Dr. Palmer enhanced my interest in the course material through her extensive teaching, engaging course material, and constructive feedback. I plan to share the knowledge I gained from this course with my colleagues.” — Susan Abraham, PT
In addition to students appreciating Dr. Palmer’s dedication to their success in the course, many students expressed that they gained an appreciation for the role of wound care in PT and were able to immediately apply these insights into their practice.
“The lessons on the normal structure and function of the integumentary system including the pathophysiology of various wounds and healing principles helped my clinical decision-making in providing quality care to my patients. Although wound care may only be a part of overall PT care in outpatient settings, it has a huge impact in the overall treatment outcomes.” — Venus Ong, PT, DPT
DPT course spotlight

DPTP 8819: Differential Diagnosis
Taught in the Postprofessional Doctor of Physical Therapy online program, Differential Diagnosis is a three-credit course taught by Professor Jenny Bradley, PT, DPT.
Focusing on content that is central to physical therapists’ daily practice settings, this course contains information that is especially critical for those working in the direct access states. Much of the information covered in this course isn’t taught in bachelor’s or master’s degree programs. Building on foundational skills acquired in entry-level PT programs, this course dives deeper into multiple body systems to identify areas and red flags that are outside PTs’ areas of practice that need referrals back to a physician for further diagnostic testing.
“This course is definitely central to the daily life of physical therapists. I honestly feel uncomfortable with my previous studies in physical therapy, as this type of information was not part of my training. I believe that baccalaureate degree therapy professionals should be required to take this course.” – DPT student
The information presented in the course provides a broader understanding of different body systems to improve students’ evaluation and assessment skills and can be applied immediately to their practice settings. Further, the format enables students to use their own experiences with patients to dive deeper into the body systems and reflect on how they could have provided better care, notice red flags they missed, or accomplished things differently.
This course reviews information related to differential diagnosis of the major body systems including cardiovascular, pulmonary, hematological, gastrointestinal, renal and urinary, hepatic and biliary, endocrine, and immune systems. In addition, students are introduced to the concept of differential screening in physical therapy and an in-depth analysis of the interviewing process.
“As a foreign-trained physical therapist with only a bachelor's degree, this course opened my eyes to the many intricate diagnoses that resemble the typical musculoskeletal conditions. I do not believe we ever had a course on differential diagnoses in my undergraduate studies so this aspect of my DPT learning is appreciated.” – DPT student
This course encompasses textbook and journal article reading with weekly assignments based on the required reading, quizzes, and discussion boards centered around students’ clinical experience, which are a favorite of students. While the course is asynchronous, Dr. Bradley offers a supplemental Zoom meeting during the course, which is an excellent opportunity for students to meet each other and discuss the course and patient cases shared in the discussion boards.
“I love teaching this course because I always learn from my students as well. I feel like it’s such an important area to focus on, especially with direct access and being a better practitioner. We might be the first medical person a patient sees, and we really need to know when something should be referred for further diagnostic testing that is outside our scope of practice.” – Professor Jenny Bradley, PT, DPT
DPT course spotlight

DPTP 8825: Extremity Manual Therapy
A standout course in the Postprofessional Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) program, Extremity Manual Therapy is designed for clinicians who are looking to expand their expertise and refresh their manual therapy skills with a focus on the extremities. Whether you’re seeking to enhance your existing techniques or dive deeper into evidence-based practices, this interactive course will provide you with the knowledge and tools to confidently apply manual therapy in a variety of clinical settings.
Taught by Drs. Jay Croswell and Adrienne Parry, this 6-week course provides a comprehensive review of manual therapy techniques for both upper and lower extremities. Students will explore a range of joint mobilizations and soft tissue techniques, guided by the latest evidence to address common musculoskeletal issues and improve patient functional mobility. The course’s structured approach ensures that learners progress through each joint systematically, building a solid foundation for effective manual therapy.
“This course is particularly beneficial for clinicians who don't regularly practice joint or soft tissue manual therapy in their clinical settings, and for those who desire a foundational understanding and immediately applicable refresher on manual therapy of the extremities.” — Dr. Jay Croswell
The course emphasizes the integration of evidence-based practice, with students engaging with current literature and applying the best available research to improve their clinical decision-making. Dr. Croswell notes, “ATSU's faculty teaches in a way that centers on the three elements of evidence-based practice: clinician expertise, patient preferences, and the application of the best available research. This ensures that students can make informed, effective decisions in their treatment approaches.”
“The hands-on manual requirements were the most valuable part of the course for me. It was a great shift from theoretical learning and gave me practical skills I could immediately apply. As soon as I had the chance, I started incorporating joint mobilizations into my clinical practice, which made a noticeable difference.” — DPT student, Kadijah Robinson, PT
Throughout the course, students participate in video presentations, where they demonstrate techniques applied to case studies, allowing for hands-on practice in a virtual setting. Active discussion forums also encourage feedback from peers and instructors, helping students refine their skills and clinical reasoning abilities.
“Most learners report that they are surprised at how much their confidence in treating patients improves in this course. Physical therapists from settings such as pediatric school-based therapies, skilled nursing facilities, and home health assignments have reported that they are able to offer their clients more options in therapy sessions.” — Dr. Adrienne Parry
This course is an excellent opportunity for physical therapists to refresh and strengthen their manual therapy skills, especially for those who haven’t practiced joint mobilizations and soft tissue techniques in their clinical settings for some time. Students leave with a deeper understanding of how to apply these interventions, and many report successfully implementing joint mobilizations in their workplace, expanding their treatment options and improving patient outcomes.
“This course taught me the proper techniques for joint mobilization and helped me understand when to apply each level of manipulation effectively.” — DPT student, Rhondeen McFarlane, PT
AT course spotlight

Applied Research Project
As part of the Doctor of Athletic Training program, the Applied Research Project (ARP) is a series of four courses students participate in to assist in the creation of their research project. The goal of the ARP process is for students to complete a project that is meaningful and that they’re passionate about.
One of the biggest misconceptions about the DAT’s ARP is that students assume they need to conduct original research. The program offers a variety of options, including original research, which makes the process unique and approachable. The ARP is catered to the individual student’s area of passion and area of meaningful change for them or in their local clinical practice setting.
Students can conduct original research, including systematic reviews and point of care research, and are always paired with an ARP advisor who is conducting research in that area. This type of project follows the typical research process: students work closely with their advisor to develop the methodology, collect the data, analyze it, and disseminate it.
“My professors were topnotch! They were supportive, patient, encouraging, knowledgeable, and demanding, all at the same time. The pulled a level of performance out of me that I didn’t know I could execute.”
– DAT graduate, Brandon H., DAT, ABD, LAT, ATC
Students can complete quality improvement (QI) initiatives to improve an identified quality gap in their practice or at their clinical practice setting. They go through the formal QI process for their project. Students are also encouraged to create case studies for interesting and unique cases they’ve come across in their practice.
The last option is a special project, which covers the whole spectrum of possibilities. Some examples include developing education intervention to provide education for a known gap in AT, creating a business proposal for employers detailing new positions or creating new programs at their employment setting, developing protocols to be adopted by employers, or developing new theoretical frameworks for clinical practice for AT education.
Check out completed student research projects at Kubify.
“We’ve seen a whole variety of different projects and it’s been really exciting to see these projects move forward beyond the ARP process and actually make meaningful change to athletic trainers and the profession.”
– Professor Cailee Welch Bacon, PhD, ATC

The four courses within the Applied Research Project include:
- ATRN 9001: Analyzing the Problem
- ATRN 9002: Proposing a Solution
- ATRN 9003: Implementing and Evaluating the Solution
- ATRN 9004: Completing and Disseminating the Project
Explore all our post-professional AT courses ›
Analyzing the Problem is the first course in the series of four courses designed to assist students with the development of an applied research project through the stages of reviewing the literature to project dissemination. The purpose of this course is to provide students with the knowledge and skills to successfully review the literature around their chosen ARP topic and write a focused review of literature, which will serve as a foundational paper for the ARP.
“After diving deeper into my literary search, I felt confident discussing the topic with people at my workplace. I was able to implement my knowledge immediately with my supervisors and my students knowing I had the most updated information.” – DAT graduate, Taelar S., DAT, LAT, ATC, CES, GTS
Proposing a Solution is the second course with the purpose of providing students with the knowledge and skills to develop and present their ARP proposal. During this course, students will work closely with their ARP advisor to ensure the ARP proposal is methodologically sound and feasible. By the end of this course, the student will have completed the ARP proposal and will present the project to their ARP advisor and submit their application to the IRB.
Implementing and Evaluating the Solution is the third course with the purpose of providing students with the knowledge and skills to continue finalizing their data collection forms and sampling methodology. This course will help students develop and implement an analysis plan for their ARP, based on previous methodological and statistical courses, and write the bulk of their results section so that they will be ready to complete their manuscript and prepare it for dissemination.
“The ARP process really increased my understanding of conducting point of care research and how beneficial it will continue to be for our profession as we continue to see evolution within the field of medicine.”
– DAT graduate, Jessica P., DAT, ATC, CES
Completing and Disseminating the Project is the fourth and final course. The purpose of this course is to provide the knowledge and skills needed to successfully complete the ARP manuscript, and to identify possible strategies for the dissemination of research findings through multiple means, such as poster and oral presentations or manuscript submission.
Many AT students can be intimidated by the research process. By providing structure via these four courses, students work very closely with their ARP advisor, and they are able to approach the project in small digestible components which make the process more feasible and less intimidating. This process enables students to get a better understanding of the steps that they can continue to take after they complete the ARP and the DAT degree to keep that process moving forward.
“Most athletic training students see research as intimidating, so if I can break down the process to simplify it for them that may help them make their project successful and less intimidating.” – DAT graduate, Brian B., DAT, LAT, ATC
Post-graduation, many students are still focused on their ARP topic, presenting at district and national conferences and publishing their work. They are also continuing to create more change either at their place of employment or more broadly for the profession.
“As a full-time faculty member in the Health and Exercise Science department, I incorporate components of what I studied into a variety of courses that I teach (Principles of Fitness Assessment, Exercise Techniques, Principles of Strength Training & Conditioning).” – DAT graduate, Kristen A., DAT, LAT, ATC, CSCS, CES, FMS-2, FCS
AT Course Spotlight

ATRN 8180: Instructional Delivery and Assessment in Athletic Training
Instructional Delivery and Assessment in Athletic Training is an essential course in the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program for athletic trainers looking to expand their teaching skills and pass on clinical expertise. This 10-week course helps experienced clinicians transition into educators, equipping them with the tools to teach in both academic and clinical settings.
“This course helps athletic trainers build or refine the skills they need to become effective educators. By focusing on foundational topics, students can implement these strategies right away in both the clinic and the classroom.” - Dr. Cailee Welch Bacon
Taught by Cailee Welch Bacon, PhD, ATC and Rachel Geoghegan, DAT, MSHRD, ATC, the course explores key topics such as adult learning theory and social determinants of learning. Each week focuses on a different aspect of education, allowing students to gradually build a solid understanding of the skills necessary for effective teaching. The course emphasizes practical application, ensuring that students can apply what they learn to real-world teaching scenarios.
“Our goal is to prepare athletic trainers to confidently transition into education. This course provides them with the tools they need to become educators.” - Dr. Rachel Geoghegan
Throughout the course, students work toward developing their own teaching philosophy, which they can use for future teaching opportunities. Assignments include weekly reflections and a long-term project where students choose an everyday skill they are experts in, and apply the weekly content to improve how they would teach that skill to others. By the end of the course, students will have a clear sense of their teaching identity and a document they can use when applying for educator positions.
“The weekly reflection posts helped me process my learning and figure out who I am as an educator.” - DAT Student, Jennifer Hudson, MEd, LAT, ATC
In addition to developing teaching philosophies, the course incorporates the use of educational technologies and tools that enhance the learning experience. Students explore tools like artificial intelligence and other educational technologies, helping them integrate digital tools into their teaching.
“I’m planning to teach an elective course next year and will definitely use the strategies I’ve gained in this class to ensure success.” - DAT Student, Jeffrey Nadeau, MS, ATC
Dr. Bacon and Dr. Geoghegan are known for their supportive and engaging teaching approach. They are always available for feedback and guidance, helping students grow as educators and providing support that prepares them to transition into higher education with confidence.
“Creating my teaching philosophy was incredibly enlightening. It helped me reflect on my core values and teaching style, giving me clarity on how to deliver more effective instruction in the future.” - DAT Student, Aaron Jackson, MS, ATC, CES, PES
By the end of the course, students will have the skills and confidence to take on teaching roles in a variety of educational settings. Whether in the classroom, clinic, or through patient education, this course provides students with the foundational tools to become impactful educators in the athletic training profession.
AT Course Spotlight

ATRN 8190: Programmatic Planning and Curricular Design in Athletic Training
Programmatic Planning and Curricular Design in Athletic Training is a 10-week course in the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program, intended to prepare students to design and improve educational offerings across athletic training settings. The course emphasizes instructional design principles, including Backward Design and Universal Design for Learning (UDL), helping students create effective, evidence-informed educational offerings that bridge theory and practice.
“We really focus on teaching students the process of instructional design, which equips them to develop educational offerings in a variety of contexts and settings.” – Dr. Barton Anderson
Taught by Dr. Barton Anderson, DHSc, AT, ATC, ATRN 8190 is an asynchronous course that follows the instructional design process. Each week includes preparatory content, a discussion-based assignment, and an individual reflection. The course uses both project-based and discussion-based learning strategies to support the application of concepts. Content progresses from individual instructional design to program-level planning and assessment, with a final project that showcases student's instructional design knowledge and skills.
“What I found insightful about this course was the broader scope of planning an entire curriculum to fit standards for accreditation. Professor Anderson is knowledgeable and compassionate. He clearly has a passion for AT education.” - DAT Student, Summer Blunden, ATC, M. Ed
Throughout the course, students complete activities that build toward the development of a real-world educational experience. By the end of the course, they leave with a comprehensive understanding of instructional design that can be applied across clinical or academic settings. The biggest benefit is gaining confidence and clarity in how to design learning that is purposeful and impactful.
“I enjoyed the final teaching project where I was able to take all the components we learned throughout the course and create my presentation. My teaching style has expanded and is much more active allowing for students to develop critical thinking skills and reasoning.” - DAT Student, Jennifer Hudson, M. Ed, LAT, ATC
As students progress, they build the skills necessary to assess and refine educational programs, ensuring that they remain relevant and effective. These skills are invaluable for those aiming to take on leadership roles, whether in higher education, clinical teaching, or program development. The course prepares students to not only design effective curricula but also to continuously improve them based on feedback and data, promoting an ongoing cycle of growth and enhancement in athletic training education.
“Students who are seeking future positions in athletic training education or who seek to improve their knowledge and skills as educators or preceptors will benefit from the information provided in the course. “- Dr. Barton Anderson
AT Course Spotlight

ATRN 7430: Orthopaedic Imaging and Labs
An intensely informative course in the Orthopaedics track and graduate certificate of ATSU’s Athletic Training Department, the Orthopaedic Imaging and Labs course is designed to increase the AT’s knowledge in imaging and laboratory techniques to evaluate and treat orthopaedic patients. This course can also be taken as a part of the Master of Science in Athletic Training (MSAT) degree or the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program.
Students are exposed to a variety of imaging modalities including radiographs, magnetic resonance imaging, CT scans, and musculoskeletal ultrasound. These are examined along with common lab tests and results along with specific scenarios as arranged by course instructor and adjunct professor JJ Wetherington, MS, LAT, ATC, BCS-O and supported by assistant professor and course facilitator Nicolette “Nikki” Harris, DAT, LAT, ATC, CSCS.
Professor Wetherington emphasizes that the biggest gain students can anticipate from the course is an abundance of practical knowledge and a new skill set.
“This course significantly expands a learner's knowledge in orthopaedics and diagnostic imaging. It gives students a chance to learn by studying real world, practical examples. They truly develop an additional skill set that a lot of athletic trainers don't have.” — Professor JJ Wetherington
Students especially appreciate the opportunity to review and learn from an expert currently working in the field and are eager to absorb all knowledge that can be gleaned from Professor Wetherington as well as any imaging examples he shares. The practical experience gained from studying these images is invaluable.
“I was able to directly implement a lot of the information in this course because I use ultrasound in my regular clinical practice. Being able to better understand how to read images has drastically improved my ability as a clinician to evaluate and diagnose complicated injuries in my patients.” — Mitch Barnhart, DAT, ATC, AT
Many students feel the course is applicable immediately to their AT practice.
“I loved getting the opportunity to dive deeper into reading imaging to be able to translate that into practice when reviewing MRIs in clinic with patients.” — Abby Gullo, MS, ATC, CSCS
Much of the course is arranged around compiling information and references for students to use in their own practice or share with peers, as well as creating patient educational materials.
“I continue to utilize some of the resources that I created in class to enhance the verbal education that I give to patients and their families. I enjoyed learning about interpreting imaging and lab reports. Right away, I was able to incorporate what we were learning in class about imaging of the elbow to identify a subtle fracture that had been missed in one of my patients.” — Kendall Marshall, DAT, ATC, CSCS
Discussion is also a key part of the course, as talking about orthopaedic imaging concepts with other ATs helps students increase their comfort and practice the new “language” learned in the class.
“Regardless of what their role is in imaging, this course gives ATs kind of a new language to speak — particularly during the evaluation process or when they're communicating in an interdisciplinary capacity with a physician or other medical professionals. ATRN 7430 is really giving them a new language so that they can be comfortable when talking about a condition.” — Dr. Nikki Harris
AT course spotlight

ATRN 7440: Orthopaedic Surgical Considerations

Taught as part of the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program, the post-professional Master of Science in Athletic Training (MS-AT) program, and the Graduate Certificate in Orthopaedics, the Orthopaedic Surgical Considerations course is designed to enhance the athletic trainer’s knowledge, understanding, and awareness of special considerations for rehabilitation following common orthopaedic surgeries. With a focus on improving ATs’ ability to provide quality education and counseling to orthopaedic patients, students develop advanced knowledge and skills in post-surgical rehabilitation.
Within the first couple of weeks of the course, basic concepts related to orthopaedic surgery and sports medicine, and general guidelines for rehabilitation considerations for post-surgical patients are presented. This sets the framework for the general process of understanding surgery and how ATs manage post-surgical patients.
“This course brought to life the intricacies of orthopaedic surgery and the rehabilitation considerations that follow. We got to learn collectively about common major orthopaedic surgeries. This course has helped me be able to better describe what a patient may be going to experience. It has also allowed me to engage in better rehabilitation understanding.” – DAT student, Caitlyn T., MS, LAT, ATC
Then curriculum then focuses on 10-12 specific procedures in different body regions that are common in athletic training, from a week on arthroscopic surgery at the hip to ACL reconstruction. Then, discussion covers how to guide the progression of post-surgical rehabilitation based on evidence, inclusive of tissue response to surgery, post-surgical rehabilitation guidelines and timelines, and surgical outcomes.
“While the final project was a lot of work, it was very rewarding to become intimately familiar with a surgical procedure and rehabilitation process that I was interested in. Otherwise, the discussion board assignments were all equally valuable.” – DAT student, Kim D., MS, LAT, ATC
Focusing on what ATs need to know about orthopaedic surgery, the goal of this course is to ensure they can provide quality care for the patient, progress the patient as appropriate, and maintain and protect the surgical procedure as it’s healing. Students will engage in weekly collaborative learning activities to critically appraise the current evidence for post-surgical rehabilitation approaches.
“All of the patient education assignments were my favorite, as they have been something I have formally used in my clinical practice. Patient education material has helped me manage patient expectations and appropriately educate and discuss their options.” – DAT student, Matt S., ATC, MA, CSCS
The course culminates with the development of a comprehensive, evidence-based post-surgical rehabilitation protocol for an orthopaedic surgery of the student’s choice. The biggest benefit of this course is exposure to and increased awareness of a wide variety of common sports medicine and athletic training orthopaedic procedures. The course prepares students to be able to perform surgical rehab after any type of surgery, even if it isn’t a surgery covered in the course.
“Beyond the discussion boards, I really enjoyed having to create a post-operative rehab protocol. That is something I had never done before and had previously relied on pre-existing documents in the literature or from the physician.” – DAT student, Kendall M., MS, ATC, CSCS
The DAT program attracts a variety of ATs from different backgrounds and clinical experiences, and this course is no different. For students who aren’t working in post-surgical rehab on a regular basis, they still benefit from this course by gaining a much deeper understanding of the surgical process and rehab, enabling them to better educate and help their patients navigate the process. And for students who work in post-rehab, this course offers directly applicable knowledge to their practice.
“Throughout the course, I had patients with a UCL reconstruction and another patient with an ACL reconstruction which gave me the ability to immediately implement what I learned and how to properly help them.” – DAT student, Anna F., MS, ATC
The Athletic Training Department at ATSU has the goal of creating courses that provide foundational content to support the student in continuing to develop and grow as a clinician throughout their career. Most students who take this course have little exposure to surgical procedures or post-surgical rehab and have never taken a course focused on different surgical procedures. This course helps expand that area of knowledge from a clinical skills standpoint and from a patient education standpoint.
AT course spotlight

ATRN 7150: Clinical Scholarship in Athletic Training
A foundational course for ATSU’s Athletic Training programs, Clinical Scholarship in Athletic Training is designed to strengthen students’ ability to interpret and generate evidence in clinical practice. Taught by professor Cailee Welsh Bacon, PhD, ATC, FNATA, FNAP, this course is one of the first students encounter in the Master of Science in Athletic Training (MSAT) program, the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program, and the Graduate Certificate in Clinical Decision-Making in Athletic Training program. This course establishes the skills and mindset needed to navigate evidence-based practice and practice-based research while applying them directly to patient care.
Offered in a 10-week block, the course provides an immersive learning experience designed for students with varying backgrounds. It embraces competency-based education principles, allowing students to progress at their own pace while adjusting to the asynchronous online environment. Students work through Personalized Learning Pathways (PLPs), weekly content, and a multi-week infographic project that helps translate research into clear, practical tools for peers, patients, and colleagues.
Assignments include a blend of reflective, analytical, and creative tasks that mirror the real demands of modern clinical practice. The structured PLPs guide students through content, offering opportunities to check understanding and solve problems. Many enter the course expecting a traditional evidence-based practice review but quickly discover its broader purpose.
"In the very first week, we strip away misconceptions about EBP and discuss how evidence-based practice should truly look in clinical practice. Students begin to see themselves not just as clinicians, but as emerging clinician-scientists whose everyday decisions can shape better patient care.” – Dr. Bacon
The course also encourages students to challenge long-held habits in clinical reasoning and embrace new approaches.
"Unlearning is a crucial skill for any healthcare professional, and students in this course begin their practice of unlearning in Week 1.” – Dr. Bacon
Students often highlight the infographic project as a particularly meaningful assignment because of its creativity and real-world application. The project gives students the chance to synthesize research and communicate it in a format that can be immediately used in their workplaces.
"It allowed me to take research and translate it into a clear, visual tool that I could use to communicate important topics like burnout or injury prevention with administrators, coaches, and parents in my school. It was practical, creative, and directly applicable to my role.” – AT student, Lindsay Blanford, ATC
Many students also emphasize how the course has directly influenced their professional practice. They report that the tools and skills they learn, including evidence appraisal and infographic creation, help them advocate for their roles and improve communication with colleagues and patients.
"It gave me an opportunity to apply research practices in creative, meaningful ways. What I learned was immediately useful, and I was able to bring those tools directly into my current job.” – AT student, Callie Tosh, MAT, LAT, ATC
For Dr. Bacon, teaching Clinical Scholarship in Athletic Training is especially rewarding because of the transformation she sees in students.
"Students begin to understand their role within the broader healthcare landscape and their value as a clinician-scientist in advancing patient care. Watching them become more confident, more curious, and more intentional in their thinking is incredibly rewarding.” – Dr. Bacon
AT course spotlight

ATRN 8100: Practice-Based Research
Practice-based research represents the last step of the transnational research continuum and is vital to the translation of evidence into routine clinical practice. Taught in the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program, Practice-Based Research is one of the last classes students take before graduating with their doctorate. The course allows students to reflect on previous curriculum and see how they can apply learned concepts in their clinical practice to improve their understanding of and ability to conduct practice-based research.
"Interestingly, the course in its entirety was my favorite. After the course, our emergency department implemented a number of the course items to initiate research in the department.” – DAT graduate, David H., DO, DAT, ATC
As one of the few athletic training programs that offer a specific course for practice-based research, many topics discussed typically aren’t found in athletic training curricula, such as the clinician-scientist model, researcher-clinician partnerships, common study designs and statistical approaches for point-of-care research.
"I learned a more progressive way to conduct research at the point of care and to answer clinical questions, which I found beneficial. I also learned how the AT-PBRN can be utilized by clinicians for integrated use of the EMR system to promote research clinicians in the profession of athletic training.” – DAT student, Jerry S., MS, ATC, LAT
The first half of the course is heavily structured with readings and discussion boards, while the second half of the course is dedicated to students designing a point-of-care research project. While implementing the project isn’t mandatory, it enables students to think about what they can do at the point of care in terms of research and how they can design a study to create practice-based evidence and disseminate their findings to patients.
"I enjoyed completing the practice-based research project that encompassed a topic of interest and how it impacted the clinician-patient care. I began incorporating tools based on the research to improve patient care and provide valuable information for the clinician.” – DAT student, Adriana P., MS, LAT, ATC
Practice-Based Research is taught by Kenneth C. Lam, ScD, ATC, who’s an associate professor of clinical research within the Department of Interdisciplinary Health Sciences and serves as the director of the Athletic Training Practice-Based Research Network (AT-PBRN), which is the only practice-based research in athletic training recognized by HARQ.
"If we look at practice-based research in athletic training, our faculty are leaders in that regard. We want our students to have the skills and knowledge to make the last step of the translational research framework because it is vital for all care of patients in terms of research evidence.” – Dr. Kenneth Lam, ScD, ATC
AT course spotlight

ATRN 8170: Applied Clinical Education and Mentoring
Taken as part of the Doctor of Athletic Training program or the Athletic Training Education Certificate program, the Applied Clinical Education and Mentoring course is intended to improve students’ understanding and application of best practices in clinical education and mentoring in athletic training professional education and residency or fellowship programs.
Course content is structured through assigned readings, guided questions, and online discussions that help foster students’ engagement. The first half of the course focuses on fundamental information, including the history of clinical education in healthcare overall, before narrowing in on clinical education in athletic training. Weekly topics incorporate best practices for bridging the gap between didactic and clinical education, clinical education techniques and models, preceptor mentoring, and student/resident/fellow mentorship models. The class then discusses prevalent stakeholders and their roles.
The second half of the course covers the application of information learned with focused discussion regarding developing assessment activities at the point of care to facilitate practice-based research.
“This course taught me practical ways to mentor future generations of ATs. It also helped me utilize new skills to be a better preceptor to athletic training students. I will be able to implement the knowledge from this course in the coming months as my workplace becomes a clinical site for a local AT education program.” – DAT student, Cody W., MS, LAT, ATC, CSCS
Then, the course delves into contemporary topics in athletic training clinical education, for example, full-time clinical education experiences, facilitating transition to practice, using simulation to improve education opportunities for students, and mentoring. Students also complete a five-week long project that can either be a professional development workshop for preceptors or an assessment plan for clinical education.
“I enjoyed responding to the preceptor questions and seeing how others would respond to the issues. I made it a point to incorporate the standards into my preceptor work (teaching students why).” – DAT student, Kelly F., MS, ATC, CSS
This course is taught by Chad Clements, MS, ATC, associate professor and Director of Clinical Education, and co-taught by associate professor Bart Anderson, DHSc, AT, ATC. Prior to joining the ATSU faculty full-time in July, Chad Clements developed the course content and taught this course as an adjunct faculty. Dr. Anderson serves as the primary clinical faculty member and clinical education coordinator for the post-professional master’s program, overseeing all aspects of the Advanced Clinical Practice program (Clinical Education), including establishing and maintaining graduate assistantships, coordinating affiliated clinical sites and preceptors, and providing clinical mentoring to AT program students.
“Each of our own lived experiences has shaped what we know about being a student in a professional AT program and going through clinical experiences. This class helps reflect on the successes, the challenges or failures of students’ own experiences, and how can they now improve the experiences students have in professional AT programs.” – Professor Chad Clements
Since all students experienced a professional athletic training program, many relate to the post-professional curriculum. Most students in this course have been practicing clinically, possibly in the role of a preceptor, but may not have any experience looking at the standards for accreditation for AT programs and what the specific content is related to in clinical education. For students who are already in faculty roles, this course helps expand on their ability to effectively implement a structured clinical education framework.
AT course spotlight

ATRN 7110: Quality Improvement and Patient Safety

Quality improvement is the consistent, combined effort of many to make changes in healthcare that will improve patient outcomes, system performance, and professional development. Taken as part of the Doctor of Athletic Training (DAT) program, Master of Science in Athletic Training (MS-AT) program, and post-graduate certificate in clinical decision-making, this 10-week course is designed to enhance the athletic trainer’s understanding of quality improvement as it relates to patients’ health, clinical care, and learning.
“This class had me taking a second look at a lot of different protocols that my institution has in place and how to improve upon them, not only that, but it also gave me the tools and the knowledge I needed to know how to properly and effectively go about it.” – DAT student, Mackenzie V., MS, LAT, ATC
Students are introduced to an element of quality improvement each week, building upon previous concepts. Starting with a global overview of the history of quality improvement, students are then introduced to the methodology used for quality improvement, the Model for Improvement, which serves as the theoretical foundation for the course. Curriculum topics include creating and managing interprofessional teams, identifying quality improvement issues, process literacy, data collection for continuous improvement, and implementing system changes.
“It is a more systematic approach rather than just writing ideas down. The step-by-step approach to making change is something that takes time and does not happen overnight. I have learned to incorporate others in the process as well.” – DAT student, Brian B., MEd, LAT, ATC
Students are introduced to tools and strategies to become process literate, which helps clinicians better understand what’s going on within their healthcare system to see where the opportunities are to make it better. During the course, students will also be introduced to common tools used in quality improvement projects, such as process diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, run charts, and plan-do-study-act cycles.
“My favorite week was the week where we discussed working styles and how to build a team. I always see many problems in our field, but never know where to begin to address them and it becomes overwhelming. But Dr. Valier guided us through the steps on how to make change happen. Building a team and outlining each of the roles each member needs to contribute for success was something that I think is the most important.” – DAT student, Jeremy A., MA, ATC
The thread that runs through the entire course is the development of a quality improvement project. Students learn how to identify a problem or a healthcare quality gap and find ways to reduce that gap and make systems function or work better to create a better patient experience. Within the coursework, students identify an area of improvement needed within their healthcare system and create a plan for how they could make that area better. Assignments include readings, multi-media presentations, discussions, and individual and/or group assignments.
“The final project was my favorite part of the course because it put everything together. I was able to utilize the class project in my practice at the time.” – DAT student, Brian B., MEd, LAT, ATC
Some course highlights include a greater understanding of how to form and lead a team, how to take action on things that need quality improvement, and how to practically promote a culture of change.
This class has significant student and faculty interaction and sharing of ideas between students, adding a fun engagement element to the class. This course is taught by Dr. Alison Valier, PhD, ATC, FNATA, who also serves as a professor in the Department of Interdisciplinary Health Sciences and is the assistant director in the Department of Research Support through the Division of Research, Grants, & Scholarly Innovations.
“My experience with Dr. Valier was very pleasant and thought-provoking. I was excited to learn more from her. There was so much that I was excited about that I even met with her one on one via Zoom. She was responsive, patient, and very knowledgeable. One of the top professors I've had here at ATSU.” – DAT student, Jeremy A., MA, ATC
AT course spotlight

ATRN 7250: Rehabilitation Considerations for Sport Performance

Rehabilitation Considerations for Sport Performance provides ATs with advanced knowledge on how to bridge the gap from rehabilitation to sport performance. Taught by Sue Falsone PT, DPT, MS, SCS, ATC, CSCS*D, COMT, RYT, and referencing the textbook, Bridging the Gap from Rehab to Performance, written by Dr. Falsone, the course lays out an organizational system for treating an athlete from rehab back to performance. This course can be taken as part of the Master of Science in Athletic Training program, Doctor of Athletic Training program, and Graduate Certificate in Rehabilitation. Notably, it allows for the individuality of the clinician. Dr. Falsone says, “What we do is an art based on science. It allows the clinician to still be an artist, but provides them organization and science to back up what they’re doing each step of the process.”
The course covers neuromuscular considerations such as psychomotor and somatosensory control, in addition to considerations for strength training, time under tension, power development and athletic movement prescription.
“Learned a good amount of advanced rehab techniques as well as proper assessment and progression and I improved rehab knowledge. I loved the videos, projects, and the feedback we were able to give to each other.” – DAT graduate, Amanda H. DAT, ATC, CES, SMTC
Broken into weekly components, material covers identifying the pain generator and discussing the source of someone’s pain, followed by discussion on the cause of someone’s pain. The following sections covers cycle motor control, with in-depth discussion on the brain-body connection. Then the nervous system is covered, including how do to manipulate the nervous system to create an outcome of movement, such as the visual, vestibular, or co-receptive.
“My favorite assignment was creating the movement analysis chart. It made me look deeper into the types of movements each sport does and understand the types of functional movements that need to be incorporated while rehabbing to improve performance.” – DAT student, Americus W. MSAT, LAT, ATC
Then strength and power production are discussed with focus on how to manipulate sets and reps to stimulate a physiological response. Then fundamental movement patterns and understanding patterns to create movement within sport. Lastly, a discussion on the technical aspects of this process, such as how to work with coaches and technical coaches to better understand the game.
“The movement analysis project was my favorite! Essentially, I had to take one skill (I used a basketball layup) and break it down into the essential movements of the skill. This was helpful because it breaks down a play into individual movements that can be trained before training on the skill as a whole. I had a lot of fun on all of the assignments in this course because they were all so immediately applicable!” – DAT graduate, Jesse M. DAT, MS, MEd, LAT, ATC, CSCS
Woven throughout the course is discussion on the different biosocial factors that impacts the individual. Every athlete has a different story, where they are in their career, the rehab process, amount of family support are all things that impact their journey.
“My passion lies with helping athletes from preinjury through postinjury to performance. In the course of 10 weeks, the class takes learners through that process in a very organized way. It really helps the learner fill in the gaps and it highlights areas of strength in the bridging the gap between rehab and performance process, but it also highlights the areas where they need more work or need interprofessional relationships for the betterment of their patient/athlete/human.” – Dr. Sue Falsone, Professor
A lot of information is covered this 10-week course! Through a variety of assignments, including writing or a discussion board, every topic along the way of rehabilitation to performance is covered with allotted time for reflection. Following this course, ATs will be able to develop a comprehensive program for the athlete who is returning to sport post-injury.
“The faculty was a 10/10. Sue and Dr. Hortz are two of the best in the business and their expertise and experiences made the class enjoyable and challenged me to become a better clinician.” – DAT student, Brian B. M.Ed., LAT, ATC
AT course spotlight

ATRN 7340: Assessment and Management of Complex Patients with Concussion

Assessment and Management of Complex Patients with Concussion provides a thorough examination of the treatment of patients with complex medical concerns who suffer a concussion. With specific attention focused on the patient’s past medical history and co-morbid factors, students discover how these may influence the assessment, treatment, and management of head injuries. The course is focused on getting patients active using treatment strategies to assess and manage the concussion to try to get them back to their sport, job, school, even return to military duty in a much more active manner.
“I learned how to evaluate and manage complex concussion cases in ways that immediately helped my clinical practice.” – DAT Student, Maurice I., MS, ATC
As part of the Sport Neurology and Concussion track, students can take this course as a part of Master of Science in Athletic Training program, the Doctor of Athletic Training program, or the Sport Neurology and Concussion certificate program. This course is offered during Spring Block 2, and can be taken from March to May.
Starting off with a broad discussion of the biopsychosocial model of healthcare with respect to concussion and defining the complex patient, this course then focuses on one concussion subtype or clinical profile in one-week intervals. The course discusses an important profile, sleep, managing sleep, and treating sleep issues. This is followed by aerobic exercise and the importance of getting patients active at a sub-symptom threshold level early. Rehabilitation strategies for vision and vestibular deficits are discussed, followed by executive functioning and cognitive therapies. The final weeks of the course address mental health concerns, long-term consequences and medical disqualification, ending with a focus on patient-centered care. The next lecture topic is patient-centered care and how to incorporate that into concussion. A week is also spent on the long-term consequences of concussions and how to make tough decisions, like when to recommend medical disqualification to patients who are either having prolonged recovery or had multiple concussions.
“The information provided each week was relevant and easily transferable to the daily treatments of concussive patients. Each week there were many takeaways which allowed for better overall care of student-athletes. An example would be the week three project, which involved creating a sleep pamphlet. I still have this available to share with our student-athletes.” – DAT Student, Chuck M. MS, ATC
“I loved the public health concern unit. I also felt the project was very useful is combining the course material into a care plan.” – Certificate Graduate, Taeopae W., MS, ATC
Taught by Tamara McLeod, PhD, ATC, FNATA, this course offers up-to-date, evidence-based insight into related areas of complex concussions, such as mental health, public health education, and visual and vestibular rehabilitation. Dr. McLeod states, “I find with this course, every time I teach it, I’m almost restructuring it because the evidence that’s coming out to support some of these treatment modalities changes and so it certainly challenges me as an instructor to stay on top of the literature. You see a lot of lightbulbs go off in the students over the course of the 10 weeks.”
“[After taking this course], we added early active aerobic exercise and visual/vestibular rehabilitation techniques into our concussion protocol, as well as developed a solid return to learn protocol for the district.” – DAT Student, Stephanie T., LAT, ATC
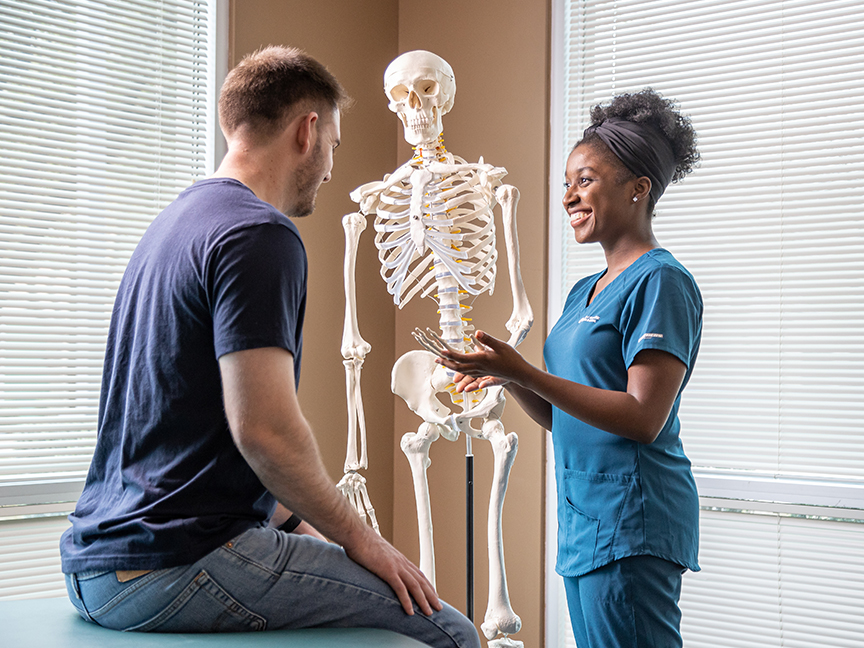






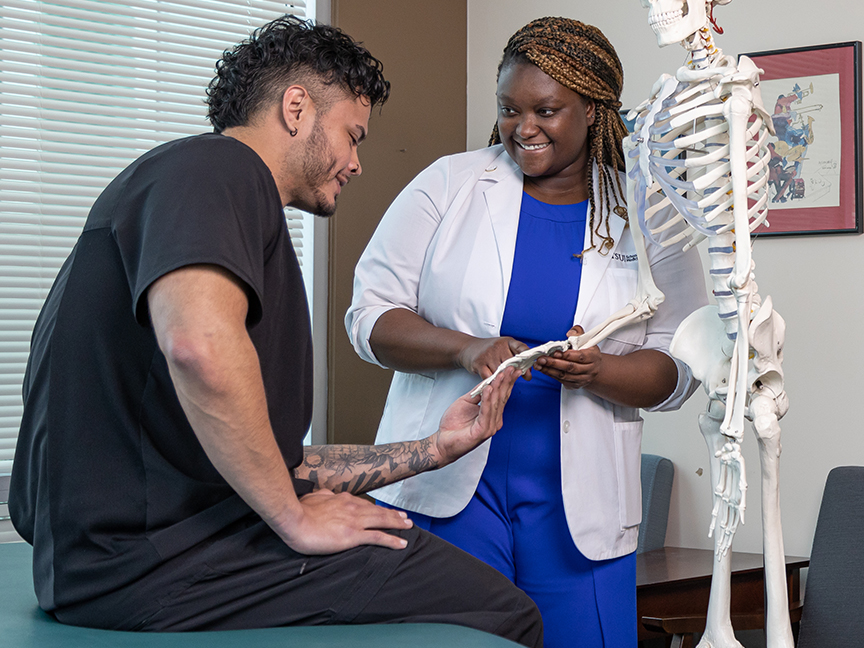
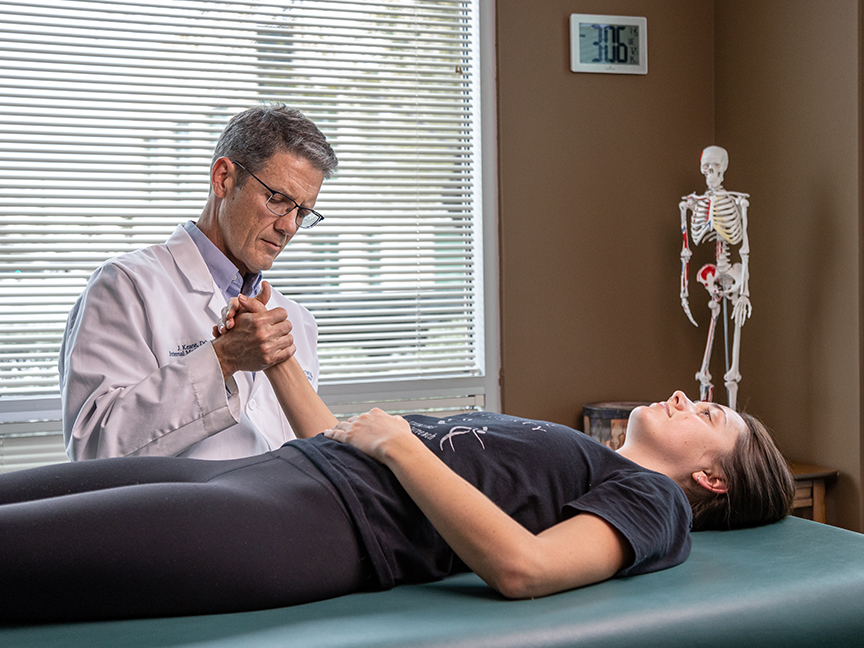
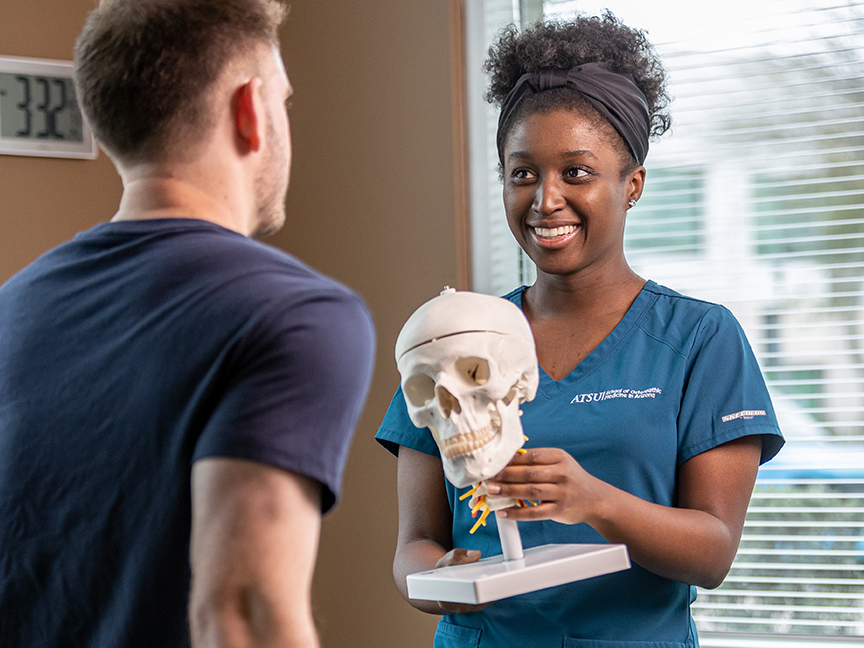























.png)






